When using both mechanical and electronic devices, it must be checked whether it is suitable for the conditions of the environment to be used. Otherwise, the devices may break down and may cause serious damages to other integrated systems.
Well, how can we know does the device suitable for the conditions of the environment to be used? Of course, we have to investigate the device’s technical features from the user manual.
In the user manual, have different technical features depends on device type. Technical features like size, weight, operating and storage temperature, in addition, according to the type of device the supply voltage, internal resistance, alarm current, etc. are frequently found in the user manual. One of the most common technical features is the IP protection class. Alright, What is IP protection class? How does it read and evaluate?
The extension of the IP code refers to “Ingress Protection” and “International Protection” in international sources. For all over the world, the IP protection class coding system is specified, according to IEC 60529 standards.
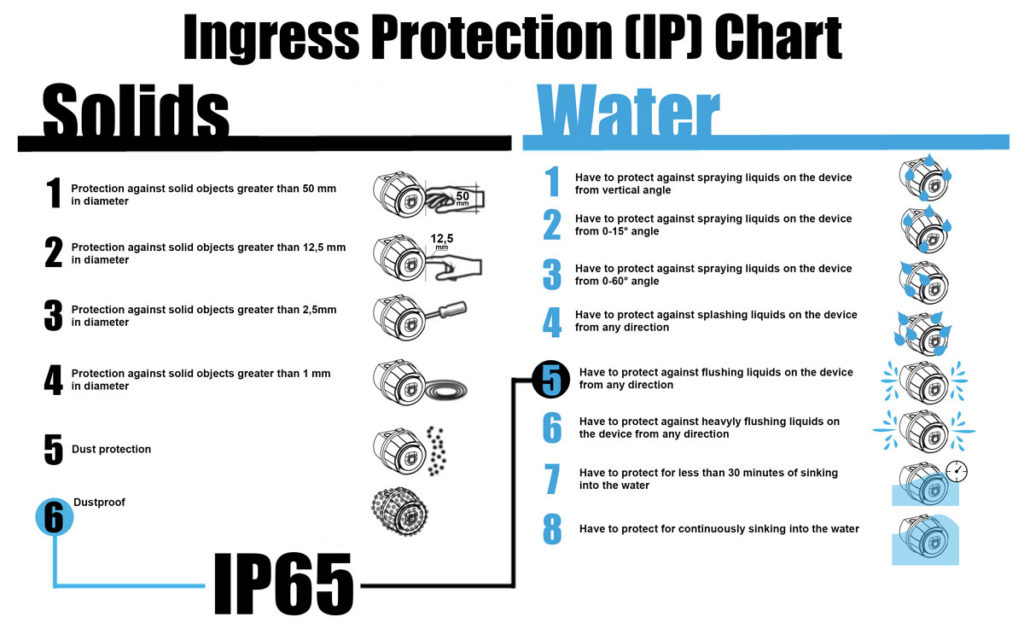
According to IEC 60529, the IP coding system has a 2-digit number next to the IP word. These numbers classify that how the device can resists the solid and liquid objects. The first order of the number shows the resistance of the solid objects. The second order of the number shows the resistance of the liquid objects.
1. Order: Resistance of the Solid Objects
| Protection Class |
Explanation |
| 0 |
Nonprotected |
| 1 |
Protection against solid objects greater than 50 mm in diameter |
| 2 |
Protection against solid objects greater than 12,5 mm in diameter |
| 3 |
Protection against solid objects greater than 2,5mm in diameter |
| 4 |
Protection against solid objects greater than 1 mm in diameter |
| 5 |
Dust protection |
| 6 |
Dustproof |
2. Order: Resistance of the Liquid Objects
| Protection Class |
Explanation |
| 0 |
Nonprotected |
| 1 |
Have to protect against spraying liquids on the device from vertical angle |
| 2 |
Have to protect against spraying liquids on the device from 0-15° angle |
| 3 |
Have to protect against spraying liquids on the device from 0-60° angle |
| 4 |
Have to protect against splashing liquids on the device from any direction |
| 5 |
Have to protect against flushing liquids on the device from any direction |
| 6 |
Have to protect against heavyly flushing liquids on the device from any direction |
| 7 |
Have to protect for less than 30 minutes of sinking into the water |
| 8 |
Have to protect for continuously sinking into the water |
Well then, how do we read and evaluate the IP protection class? For example, which environments a fire alarm siren with IP protection class IP 65 can be usable? We can examine from the table below: